What are the HTML button types and how are they different?
There are 3 types of buttons in HTML, each of them has its own purpose. In this article, we’ll inspect each one of the HTML button types and see how they are different.
Button tag
For the button element, one of two HTML tags can be used: input and button.
<button>Click here</button>
If an input tag is used a type attribute has to be specified in order for it to appear as a button. As well as a value attribute to display the text on the button.
<input type="button" value="Click here" />
Both approaches will render a button to a page that will look the same by default, no matter the button type value. However, each browser displays a button in a slightly different way.
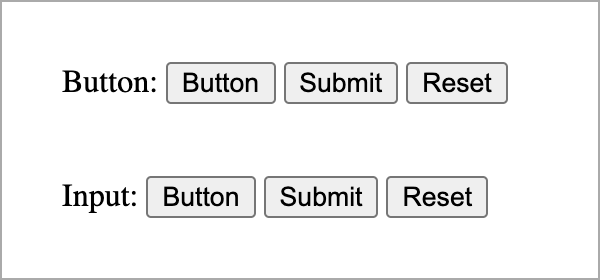
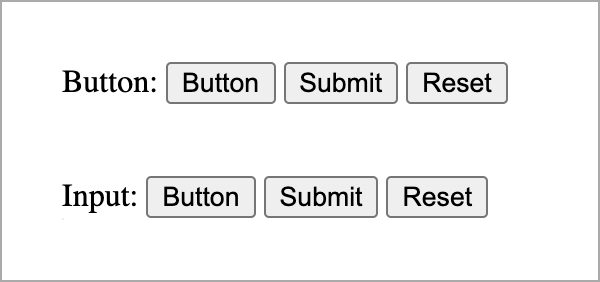

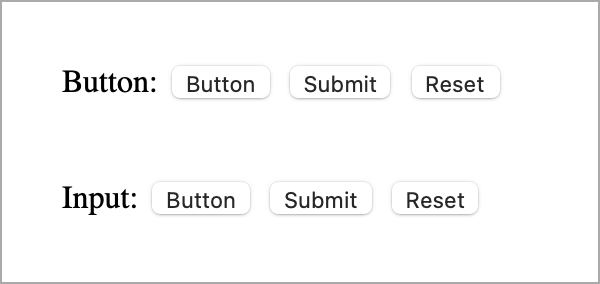
Both button and input share some common attributes:
disabledautofocustabindex
The difference between button and input tags
While button and input (when displayed as a button) do essentially the same thing, some differences exist.
- The
inputtag cannot have pseudo-element, while button can; -
The
inputtag has some unique attributes for additional functionality:- The
accesskeyattribute which allows the user to trigger a button using a key or combination of keys on the keyboard;
- The
- The
inputtag can have alabeltag attached to it.
NOTE: It is advised to use the button tag over input when possible. As button tag is fully accessible and semantic out of the box.
Button types
To set the button type, use the according attribute:
button- a regular button, doesn’t do anything unless specified (e.g. JavaScript event)submit- submits form data to the serverreset- resets the values from fields
<button type="button">Apply now</button>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
<button type="reset">Reset</button>
or
<input type="button" value="Apply now" />
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
<input type="reset" value="Reset" />
Button behavior
The type attribute defines button behavior inside the form. Visually different button types look the same and don’t have many differences.
Inside the form, once clicked the button will perform an action by default specified by the type attribute. If the button is inside the form and has no attribute specified it will act as a submit type button. If the button is inside the form and it has a button attribute, it will not trigger any actions, unless specified by JavaScript.
Outside the form, each button type acts as a regular button, this means on click nothing will happen.
Example:
<form action="">
<input type="text" placeholder="Your name" required>
<input type="email" placeholder="email@example.com" required>
<input type="number" value="42">
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
<input type="reset" value="Reset" />
<button type="button">Button</button>
</form>
Result:
Browser Support
https://caniuse.com/mdn-html_elements_button
https://caniuse.com/mdn-html_elements_button_type
https://caniuse.com/mdn-html_elements_input_input-button
